Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is an agentless solution that provides a secured database to manage privileged accounts and secrets, establishes secure sessions for users through a standard web browser and automates the execution of jobs or tasks without disclosing or sharing access.
The purpose of this guide is to perform a new installation and first time system initialization.
At the conclusion of this guide, PAM will be ready for system configuration and use.
PAM is installed to a Windows or Unix computer (physical or virtual), with optional connection to Active Directory or LDAP.
PAM consists of several modules; a database that contains secrets, configuration, passwords and audit events, a service to establish, monitor and record privileged sessions, a user directory to maintain local users and groups and a job engine to execute scripts and tasks.
Privileged Account Management
A secure AES 256-bit encrypted database that contains records which can be stored, shared and used without disclosing the actual privileged account or its secrets (passwords, certificates or keys).
Privileged Session Management
The ability to establish a privileged session to an underlying system (Windows, Unix, Linux, Mac) through a standard web browser while providing the means to monitor, join, record or terminate this session.
Privileged Job Management
Schedule, automate or execute on demand jobs to privileged systems without embedding the secrets in scripts or sharing them with untrusted users.
Software Components
To accomplish the requirements above, PAM needs to install, configure and run the following software and services.
These components are deployed during the installation process (single server deployment) or they can be distributed to multiple servers (farm deployment) to scale performance.
Single server deployments can be scaled to farm deployments when additional resources become needed.
Architectural Diagram
PAM sits within the firewall in its own SSL secured network.
Client computers make requests, establish sessions and run jobs from inside or outside the firewall to computers also located inside or outside the firewall using only their native web browser of choice.
The Database of Secrets secures all records using an AES 256-bit encrypted protocol and only delivers these secrets to authorized remote requests.
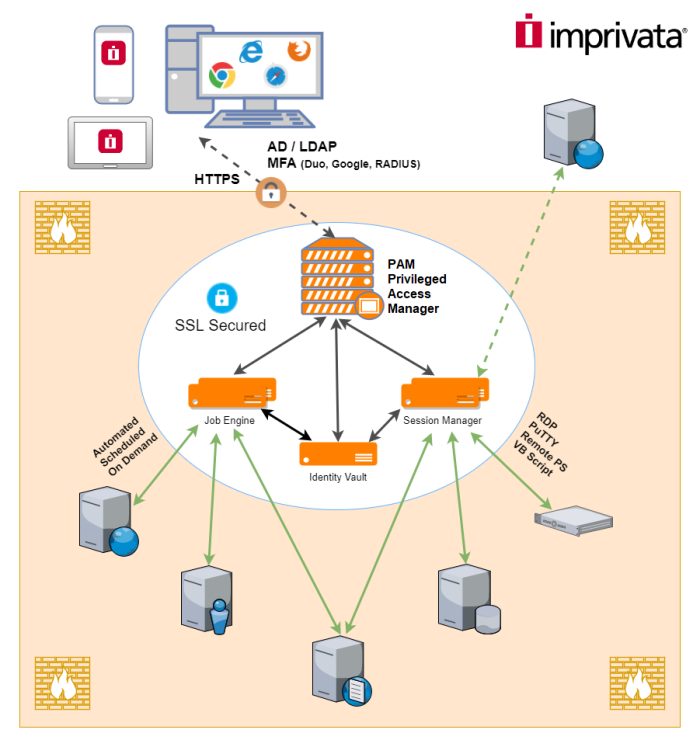
Privileged Access Management Architectural Diagram