Host Queries for Mass Script Execution
Host Queries to Configure and Execute Tasks across many Endpoints.
Say you are looking to executing a task like Local Admin Group Cleanup or Windows Service Password Reset across a series of computers, how best to configure this scenario in XTAM?
One method would be to create a record for each endpoint with its specific host, port, username and password, then apply the task to this record and setup your automated policy. A couple of steps are required, but certainly not terribly difficult to implement unless you have thousands or hundreds of thousands of assets to manage.
With that many endpoints, now you are looking into Import options. I could create a CSV file that lists all the endpoints or import them from my current session management solution like Remote Desktop Manager or mRemote. This would decrease the amount of implementation time needed to populate XTAM and get you up and running more easily, but now you have hundreds or thousands of records in XTAM that are not needed outside of task execution policies.
What if there was an easier way? What if you could execute your task like Local Admin Group Cleanup script against all your endpoints using a single XTAM record? You create a single record, you share a single record, you review and monitor a single record, but in reality that single record is executing your task against hundreds or thousands of your managed endpoints. If this sounds promising, then let’s talk about XTAM’s Host Query records.
A traditional endpoint record in XTAM defines a specific host that is used to connect to the asset. In our host query record, you define all your hosts be inputting a query to find your host rather than a host name, for instance an Active Directory query to locate your web servers. XTAM will execute your query and for every endpoint that is returned, it will queue, execute and report your configured task(s). Managing tasks for many like endpoints just got a lot easier.
Using XTAM Host Query Records
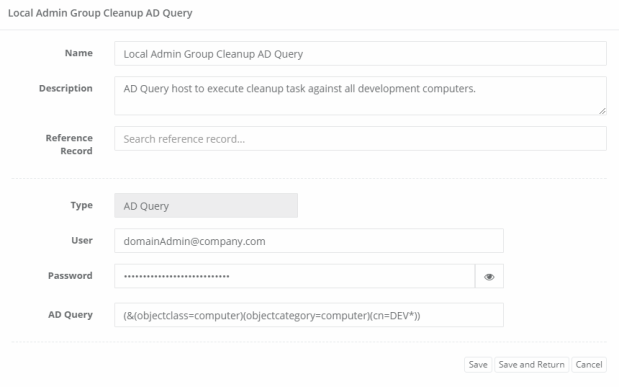
- Login to XTAM and create a new record using the type AD Query. If you do not see this type in the dropdown, navigate to Administration > Record Types, locate this AD Query type, click Edit, uncheck the Hidden option and finally click Save.
- Enter a Name (required) and Description (optional) for your new record.
- For the User and Password field, enter credentials that are will be valid for all your potential endpoints. Consider using a Domain Administrator account to avoid connection issues.
- Finally, in the AD Query field, enter an Active Directory query that will return a list of computer hosts that you want to execute tasks against.
-
Click the Save and Return button when finished.
- With the record saved, you can now apply your task(s).
- Click the Execute dropdown and then select your task from the list to execute. If you want to test the query first, select the preconfigured task Query Sample Data. This task will display a list of hosts returned from the query without executing any scripts against them. If you do not want to test the query, proceed to the next step.
-
When executing your task like Windows Local Administrator Group Cleanup, select it from the dropdown list and then you will be presented with a new dialog. In this new dialog, enter a value into the Query Sample Data Size field. This is how you determine how many endpoints to execute against. If you only want to test a subset, then enter a value like 5 which will mean only the first five returned query results like be used or enter the value -1 or All to execute the task against all query results.
-
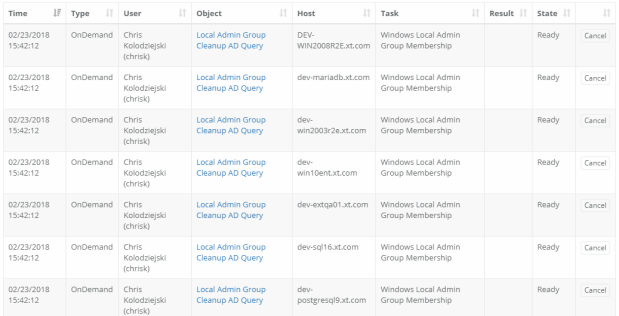
Once the task is executed, it will first generate a list of all endpoints and add them as queued jobs. You will see all these jobs listed in Job History with a status of Ready.
-
As the jobs execute, their status will update and you can review their results in the Job History or Job Summary reports.
Here is an AD Query example to return every computer in Active Directory that contains DEV: (&(objectclass=computer)(objectcategory=computer)(cn=DEV*))
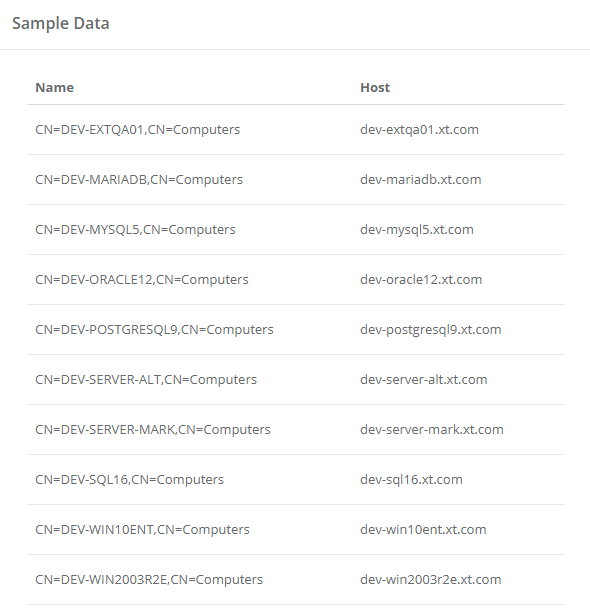
Note: When tasks are executed automatically, the AD Query will return and ultimately process all of the results. This Query Sample Data Size parameter is only available for On-Demand policy execution.

Overtime as your query returns new host results, the record will dynamically load each of these new hosts which will ensure this host query record adapts to your changing environment.